You can look at safety as the baseline for any auto manufacturer. Airbags? Check. Seatbelts? Check. But you can also look at it as crucial to a vehicle’s performance. Owners of the Subaru WRX and WRX STI understand that because the Subaru safety suite is a holistic approach that inspires driver confidence while keeping everyone in the car – and those around it – safe.
An arsenal of components, design decisions and technologies underscore this approach. Subaru vehicles offer a carefully devised combination of mechanical, electronic and structural safety technologies in the WRX and WRX STI that provide both protection and uniquely satisfying driving experiences.
Start with structure: The Subaru Ring-Shaped Reinforcement Frame serves multiple purposes. For the driver, it maximizes handling by creating a remarkably stiff base for the suspension. But it also provides occupants with proven front-, rear- and side-impact protection. WRX and WRX STI drivers and passengers are protected with an array of passive restraints, including standard Side Curtain Airbags, Front Seat Side Pelvis/Torso Airbags, Subaru Advanced Frontal Airbags and a Knee Airbag – one of seven airbags that come standard in both models.1
You might not think of Subaru Symmetrical All-Wheel Drive as a safety feature, but it definitely is one. In the WRX, the system is tailored specifically to the transmission: With the 6-speed manual transmission, the system offers Continuous All-Wheel Drive, with a viscous-coupled, locking-center differential that evenly splits torque between the front and rear wheels, delivering it where it’s needed.
Adding the Sport Lineartronic CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) brings Variable Torque Distribution (VTD) all-wheel drive system, with its planetary gear-type center differential and electronically controlled hydraulic transfer clutch. As with the manual WRX, torque flows to the wheels with the most traction, although the CVT’s system has a slight 45:55 bias to the rear wheels.
The WRX STI goes a step further with its exclusive Multi-Mode Driver Controlled Center Differential (DCCD) all-wheel drive system, with up to a 41:59 front/rear torque split and three automatic modes to finely tailor its responses to driving conditions and the road surface.
With structure and traction dialed in, let’s look to handling. The WRX features Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) with all-wheel and all-speed traction control. Three settings – Normal, Traction and Off – help drivers decide how much assistance they want from the VDC system, if any.
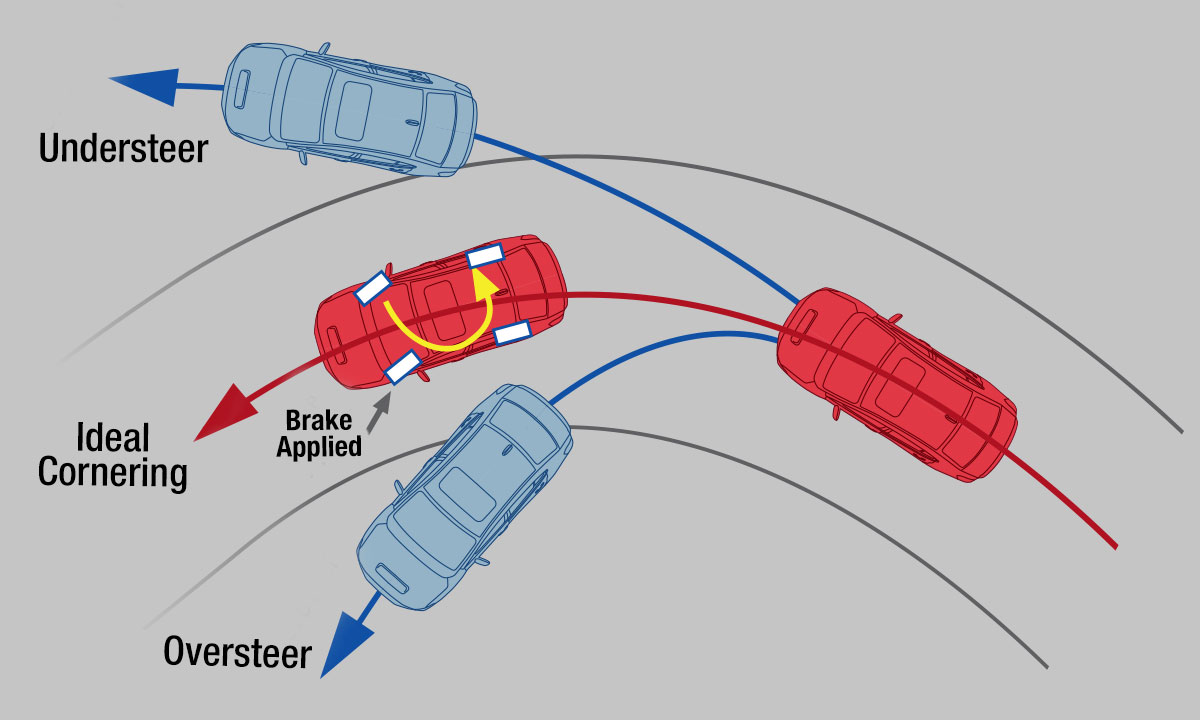
These handling aids help keep the WRX and WRX STI safe and stable, and Active Torque Vectoring (ATV) assists in reigning in understeer – where the front wheels run out of grip, and the car goes wide from the driver’s intended cornering line. ATV applies the inside wheel’s brake, which sends more torque to the outside wheel and keeps the path tight. It’s something every Subaru driver could appreciate, and has special appeal to enthusiasts for keeping the car on track.
Any discussion of safety wouldn’t be complete without EyeSight Driver Assist Technology,2 which is available on CVT-equipped WRX models. EyeSight includes Adaptive Cruise Control, Pre-Collision Braking, Pre-Collision Throttle Management and Lane Departure and Sway Warning. Also offered are Blind-Spot Detection and Rear Cross-Traffic Alert.3 Like all the safety tech discussed here, those features are invaluable for all owners, whatever they’re doing, from running errands to taking a road trip. But the Subaru commitment to safety is also what makes the WRX and WRX STI such outstanding performance cars.
1 The airbag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) affords the driver and the front passenger additional protection in moderate to severe frontal and side-impact collisions and outboard 2nd row passengers additional protection in moderate to severe side impact collisions. This system provides supplemental protection only, and seatbelts must be worn to avoid injuries to out-of-position occupants upon bag deployment and to provide the best combined protection in a serious accident. Children should always be properly restrained in one of the rear seats. See Owner’s Manual for recommended seating position. 2 EyeSight is a Driver Assist Technology which may not operate optimally under all driving conditions. The driver is always responsible for safe and attentive driving. System effectiveness depends on many factors such as vehicle maintenance, weather and road conditions. See Owner’s Manual for complete details on system operation and limitations. 3 Blind-Spot Detection, Lane Change Assist and Rear Cross-Traffic Alert are systems designed to assist the driver by monitoring the rear and side areas of the vehicle during a lane change or reversing and are not a substitute for safe and attentive driving.